
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
-
- Magnetic Resonance-Based Assessments Better Capture Pathophysiologic Profiles and Progression in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Seung Joon Choi, Seong Min Kim, Yun Soo Kim, Oh Sang Kwon, Seung Kak Shin, Kyoung Kon Kim, Kiyoung Lee, Ie Byung Park, Cheol Soo Choi, Dong Hae Chung, Jaehun Jung, MunYoung Paek, Dae Ho Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):739-752. Published online October 28, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0137
- 8,737 View
- 219 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
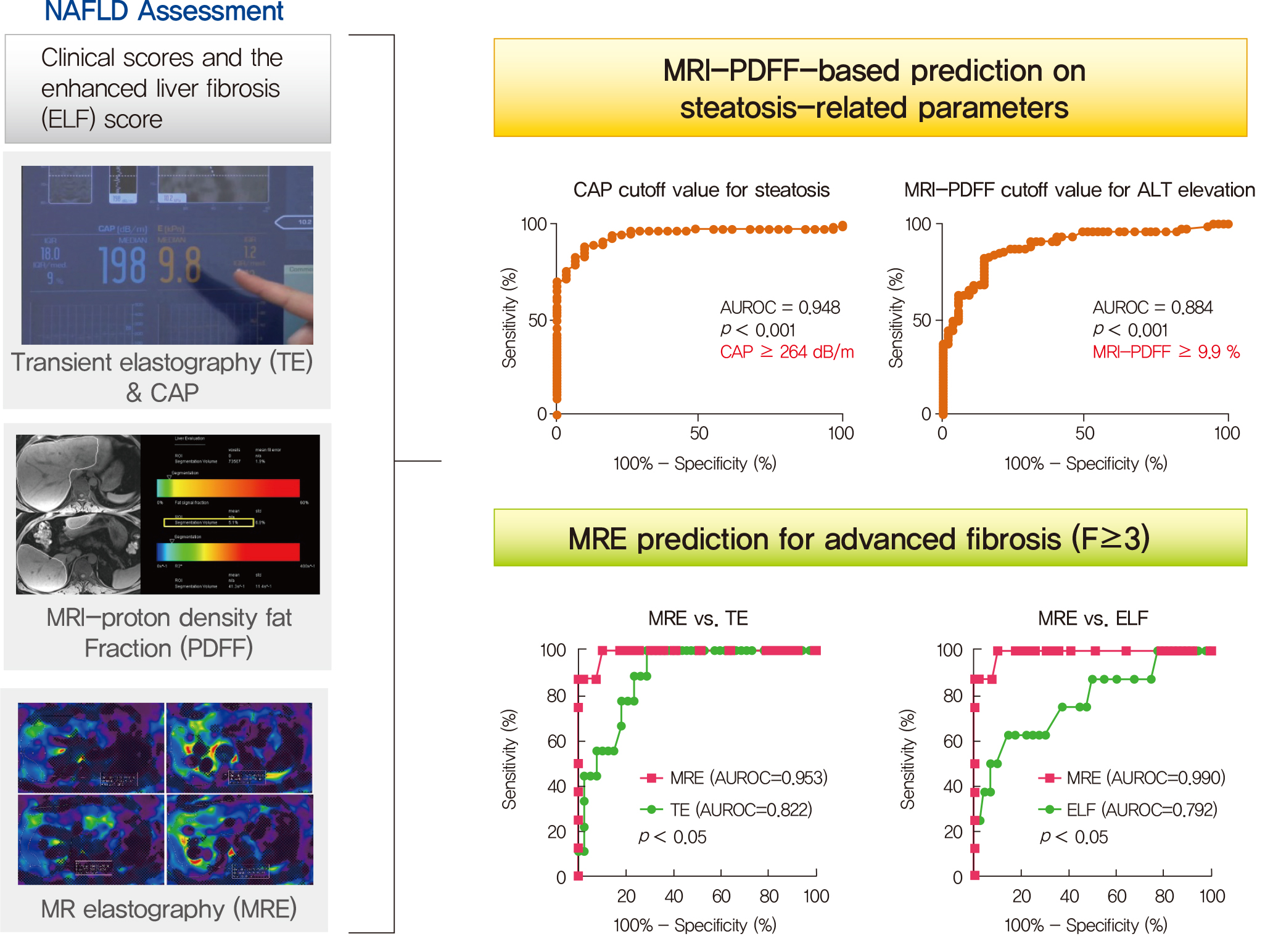
Several noninvasive tools are available for the assessment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) including clinical and blood biomarkers, transient elastography (TE), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques, such as proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF) and magnetic resonance elastography (MRE). In the present study, we aimed to evaluate whether magnetic resonance (MR)-based examinations better discriminate the pathophysiologic features and fibrosis progression in NAFLD than other noninvasive methods.
Methods
A total of 133 subjects (31 healthy volunteers and 102 patients with NAFLD) were subjected to clinical and noninvasive NAFLD evaluation, with additional liver biopsy in some patients (n=54).
Results
MRI-PDFF correlated far better with hepatic fat measured by MR spectroscopy (r=0.978, P<0.001) than with the TE controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) (r=0.727, P<0.001). In addition, MRI-PDFF showed stronger correlations with various pathophysiologic parameters for cellular injury, glucose and lipid metabolism, and inflammation, than the TE-CAP. The MRI-PDFF and TE-CAP cutoff levels associated with abnormal elevation of serum alanine aminotransferase were 9.9% and 270 dB/m, respectively. The MRE liver stiffness measurement (LSM) showed stronger correlations with liver enzymes, platelets, complement component 3, several clinical fibrosis scores, and the enhanced liver fibrosis (ELF) score than the TE-LSM. In an analysis of only biopsied patients, MRE performed better in discriminating advanced fibrosis with a cutoff value of 3.9 kPa than the TE (cutoff 8.1 kPa) and ELF test (cutoff 9.2 kPa).
Conclusion
Our results suggest that MRI-based assessment of NAFLD is the best non-invasive tool that captures the histologic, pathophysiologic and metabolic features of the disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Novel Score Based on Controlled Attenuation Parameter Accurately Predicts Hepatic Steatosis in Individuals With Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Derivation and Independent Validation Study
Zi-Ming An, Qiao-Hong Liu, Xin-Jian Ye, Qian Zhang, Hua-Fu Pei, Xin Xin, Jie Yuan, Qian Huang, Kun Liu, Fang Lu, Zhi-Han Yan, Yu Zhao, Yi-Yang Hu, Ming-Hua Zheng, Qin Feng
Clinical and Translational Gastroenterology.2024; 15(3): e00680. CrossRef - Imaging Methods Applicable in the Diagnostics of Alzheimer’s Disease, Considering the Involvement of Insulin Resistance
Petra Hnilicova, Ema Kantorova, Stanislav Sutovsky, Milan Grofik, Kamil Zelenak, Egon Kurca, Norbert Zilka, Petra Parvanovova, Martin Kolisek
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3325. CrossRef - Polyunsaturated and Saturated Oxylipin Plasma Levels Allow Monitoring the Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Progression to Severe Stages
Miguel D. Ferrer, Clara Reynés, Margalida Monserrat-Mesquida, Magdalena Quetglas-Llabrés, Cristina Bouzas, Silvia García, David Mateos, Miguel Casares, Cristina Gómez, Lucía Ugarriza, Josep A. Tur, Antoni Sureda, Antoni Pons
Antioxidants.2023; 12(3): 711. CrossRef - An individual patient data meta-analysis to determine cut-offs for and confounders of NAFLD-fibrosis staging with magnetic resonance elastography
Jia-xu Liang, Javier Ampuero, Hao Niu, Kento Imajo, Mazen Noureddin, Jaideep Behari, Dae Ho Lee, Richard L. Ehman, Fredrik Rorsman, Johan Vessby, Juan R. Lacalle, Ferenc E. Mózes, Michael Pavlides, Quentin M. Anstee, Stephen A. Harrison, Javier Castell, R
Journal of Hepatology.2023; 79(3): 592. CrossRef - Relationship between controlled attenuated parameter and magnetic resonance imaging–proton density fat fraction for evaluating hepatic steatosis in patients with NAFLD
Ziming An, Qiaohong Liu, Wenli Zeng, Yan Wang, Qian Zhang, Huafu Pei, Xin Xin, Shuohui Yang, Fang Lu, Yu Zhao, Yiyang Hu, Qin Feng
Hepatology Communications.2022; 6(8): 1975. CrossRef - Noninvasive imaging of hepatic dysfunction: A state-of-the-art review
Ting Duan, Han-Yu Jiang, Wen-Wu Ling, Bin Song
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2022; 28(16): 1625. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Pathogenesis of Sarcopenia in Chronic Liver Disease Using Liver Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Atsushi Nakamura, Tsubasa Yoshimura, Tomomi Sato, Takeshi Ichikawa
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasma Aldo-Keto Reductase Family 1 Member B10 as a Biomarker Performs Well in the Diagnosis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Fibrosis
Aron Park, Seung Joon Choi, Sungjin Park, Seong Min Kim, Hye Eun Lee, Minjae Joo, Kyoung Kon Kim, Doojin Kim, Dong Hae Chung, Jae Been Im, Jaehun Jung, Seung Kak Shin, Byung-Chul Oh, Cheolsoo Choi, Seungyoon Nam, Dae Ho Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(9): 5035. CrossRef - Contribution of a genetic risk score to ethnic differences in fatty liver disease
Maddie J. Kubiliun, Jonathan C. Cohen, Helen H. Hobbs, Julia Kozlitina
Liver International.2022; 42(10): 2227. CrossRef - Plasma Metabolomics and Machine Learning-Driven Novel Diagnostic Signature for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
Moongi Ji, Yunju Jo, Seung Joon Choi, Seong Min Kim, Kyoung Kon Kim, Byung-Chul Oh, Dongryeol Ryu, Man-Jeong Paik, Dae Ho Lee
Biomedicines.2022; 10(7): 1669. CrossRef - Updated S2k Clinical Practice Guideline on Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) issued by the German Society of Gastroenterology, Digestive and Metabolic Diseases (DGVS) – April 2022 – AWMF Registration No.: 021–025
Zeitschrift für Gastroenterologie.2022; 60(09): e733. CrossRef - Aktualisierte S2k-Leitlinie nicht-alkoholische Fettlebererkrankung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Gastroenterologie, Verdauungs- und Stoffwechselkrankheiten (DGVS) – April 2022 – AWMF-Registernummer: 021–025
E. Roeb, A. Canbay, H. Bantel, J. Bojunga, J. de Laffolie, M. Demir, U. W. Denzer, A. Geier, W. P. Hofmann, C. Hudert, T. Karlas, M. Krawczyk, T. Longerich, T. Luedde, M. Roden, J. Schattenberg, M. Sterneck, A. Tannapfel, P. Lorenz, F. Tacke
Zeitschrift für Gastroenterologie.2022; 60(09): 1346. CrossRef - Ultrasound Methods for the Assessment of Liver Steatosis: A Critical Appraisal
Dorotea Bozic, Kristian Podrug, Ivana Mikolasevic, Ivica Grgurevic
Diagnostics.2022; 12(10): 2287. CrossRef - Significance of liver fat loss in chronic liver disease: Usefulness of hepatic proton density fat fraction measurement by magnetic resonance imaging in evaluating malnutrition
Atsushi Nakamura, Haruka Okada, Tsubasa Yoshimura, Manami Deguchi, Yuei Hosokawa, Tomomi Satoh, Takeshi Ichikawa, Keiji Okuyama, Yoshihiro Yoshioka, Hitoshi Asakura
Kanzo.2021; 62(9): 525. CrossRef - Screening for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-when, who and how?
Christoph G Dietrich, Monika Rau, Andreas Geier
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 27(35): 5803. CrossRef
- A Novel Score Based on Controlled Attenuation Parameter Accurately Predicts Hepatic Steatosis in Individuals With Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Derivation and Independent Validation Study
Validation Studies
- Transcription Factor Profile by Degenerate RT-PCR/SSCP: Application in 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Treated with TNF-alpha.
- Yoo Lee Kim, Sang Hwa Lee, Young Kil Choi, Seo Yoon Chang, Yun Soo Kim, Soo Kyung Kim, Seok Won Park, Won Kun Park, Yong Wook Cho, Sang Jong Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2007;31(5):410-420. Published online September 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2007.31.5.410
- 1,749 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Several high-throughput gene analysis techniques - differential display PCR, suppression subtraction hybridization (SSH), serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE), and DNA microarray - have permitted transcriptome profiling to understand the molecular pathogenesis of multifactorial diseases. But these techniques are of no great utility regarding feasibility, reproducibility, cost, and the amount of material required for analysis. To establish more practical method for transcription factor transcriptome profiling, we combined degenerate reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and single strand conformational polymorphism (SSCP) technique. METHODS: We categorized 417 human/mouse transcription factor mRNA into 92 small groups according to homology with ClustalW method and established 92 degenerate RT-PCR including common motives of the 92 small groups with the software program of CODEHOP, Primer Premier, Amplify 1.2. Further analysis on the amplified PCR products was performed by SSCP. This system was applied for the evaluation of changes on transcription factor transcriptome of differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocyte treated with TNF-alpha. RESULTS: 82 groups and 52 groups showed amplification of PCR before and after TNF-alpha treatment respectively and 24 groups showed significant amplification difference after TNF-alpha treatment. After TNF-alpha treatment for 48 hours, mRNA expressions of group 7, 30, and 33 which include adipocyte related transcription factors such as CEBP-alpha, RXR-alpha, PPAR-gamma were downregulated and mRNA expression of group 8 including preadipocyte abundant CEBP-beta was upregulated. These results are largely concordant with the results analyzed by oligonucleotide microarray. Randomly selected single PCR bands of group 28 and 75 on agarose electrophoresis displayed additional multiple bands by SSCP and necessitated addition of this technique to degenerate RT-PCR for further analysis. CONCLUSION: It could be suggested that degenerate RT-PCR/SSCP is practical method and could be used as a screening test for transcriptome profiling of various disease states with further validation study.
Original Articles
- Proliferative Ability of Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells and Lipid Peroxidation of Red Blood Cell Membrane in Diabetic Rats.
- Sae Young Park, Hyung Joon Yoo, Kyun Soo Kim, Hyun Kyu Kim, Doo Man Kim, Jae Myung Yoo, Sung Hee Ihm, Moon Gi Choi, Sung Woo Park
- Korean Diabetes J. 1999;23(6):785-792. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,072 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Diabetes mellitus is a known risk factor for atherosclerosis, and lipid peroxidation, expression of oxidative stress, is also known to related to diabetes mellitus. The purpose of this study was to investigate the proliferative behaviour of cultured vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and the alteration of lipid peroxidation in relation to the pathogenesis of diabetic atherosclerosis. METHODS: Seven streptozotocin-induced insulin dependent diabetic Sprague Dawley rats and 7 normal rats were studied. Using enzyme method, aortic VSMCs was cultured in diabetic rats. and proliferation was compared between normal and diabetic rat. The membrane lipid peroxidaton of erythrocytes was determined by measurement of malonyl- dialdehyde(MDA), an end-product of fatty acid peroxidation with thiobarbituric acid (TBA) reaction. MDA-TBA colored complex concentration was calculated with the extinction coefficient of MDA-TBA complex at 532nm = 1.56X105cm-lM-1. RESULT: 1. The proliferative ability of cultured VSMCs was much higher in diabetic rats than in nondiabetic ones (p<0.05). 2. Compared with normal control rats, MDA concentration of diabetic rats was significantly increased (p<0.05). CONCLUSION: We concluded that proliferation of cultured VSMCs is due to oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus as a result of the increased proliferative ability of cultured VSMCs combined with increased lipid pemxidation in diabetic rats.
- Floow-up Study of Clinical and Immunogenetic Chracteristics and Basal C-peptidein Korea Young Age Onset Diabetic Patients.
- Hyun Chul Lee, Duk Hi Kim, Jae Hyun Nam, Chul Woo Ahn, Seong Kil Lim, Kap Bum Huh, Soo Yeon Nam, Seok Won Park, Young Deuk Song, Hyun Soo Kim, Jin Wook Kweon, Kyung Hee Chang, Kyung Rae Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 1999;23(3):288-298. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,200 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
This study was undertaken to observe the changes of basal C-peptide level and to compare the clinical and immunogenetic characteristics in newly dignosed young age-onset diabetics in Korea. We studied predictors effecting the change of insulin secretory capacity in these patients. METHODS: 82 newly diagnosed young diabetic patients (mean age; 23.0+7.1, M:F=46:36) were divided into 3 groups according to the initial fasting serum C-peptide level (Classification I, group 1; C-peptide < 0.6 ng/mL, group 2; 0.6 ng/mL C-peptide <1.2 ng/mL, and group 3; 1.2 ng/mL C-peptide) and reclassified by the follow-up (mean follow-up; 3.7 year) fasting serum C-peptide level. RESULTS: According to the initial fasting serum C-peptide level, 17.1% (14/82) of the patients were classified as group 1, 35.4% (29/82) as group 2, and 47.5%(39/82) as group 3. In group 3, body mass index (BMI, p<0.01) and maximal BMI (p<0.01) at onset, family history of diabetes (p=0.01) and stimulated C-peptide increment were significantly higher than those in group 1 and 2. Presence of urine ketone (p<0.01), history of diabetic keto- acidosis (p<0.01), and frequency of insulin therapy at diagnosis (p<0.01) were significantly lower than those in group 1 and 2. No significant differences in onset age, sex, weight loss at onset, HbA1c, anti GAD antibody and HLA-DR were found among the 3 groups. After certain follow-up periods, 37.8% (31/82) of the patients were reclassified as group 1, 24.4% (20/82) as group 2, and 37.8% (31/82) as group 3 according to the follow-up fasting serum C-peptide level(classification II). All of the patients in group 1 in classification I were reclassified as group 1 in classification II. In group 2, 44.8% were reclassified as group 1 and 17.3% were reclassified in group 3. In group 3, 15.4% (6/39) of patients showed a significant decrease in insulin secretory capacity and were reclassified as type I diabetes, and their predictors for decreased insulin secretory capacity were low BMI at onset, low slimulated C-peptide increment, and antiGAD antibody. CONCLUSION: Our study showed that classification of newly diagnosed young diabetics by fasting C-peptide level is not always easy. Therefore follow-up measurement of C-peptide and consideration of clinical characteristics are needed in discriminating the type of diabetes in these groups of diabetics in Korea.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





